Because security does matter
I can say that I’ve seen thousands of Jenkins masters. The non enterprise ones are usually triggering the builds via GitHub webhooks. You can do this via the GitHub Plugin. It’s mandatory to allow github to reach your jenkins master if you want to use this method. But there is a trade-off. Security vs. comfy webhooks…
The enterprise masters are mostly using SCM polling instead, because their jenkins masters are not available from the external network. GitHub can’t reach their master. This is a show stopper, if you want to trigger a build immediately after a git push.
Although using frequent SCM polling on hundreds of repos will cause huge I/O and CPU overload on your jenkins masters, so this blog post is mostly for Enterprise Jenkins customers and for the ones who want to secure and lock down their jenkins.
The proper way
Luckily there is a plugin out there for a long time, but for some reason it remained unnoticed until now. The anonym plugin statistic says there is around only 457 installations for this plugin. How come? What is this plugin?
This mighty plugin is called the GitHub SQS Plugin
This plugin integrates Jenkins with Github projects via Amazon’s Simple Queue Service.
- Consumes a message from an SQS Queue and triggers any jobs that have a matching github repository configuration.
- Automatically adds and removes the Github SQS Service hooks.
- Trigger build job using GitHub Amazon SNS service hook that use a SQS topic subscription.
Ohh, but this is super cool. Jenkins is simply polling an Amazon SQS queue. This does not cause I/O at all. If there is a git push, GitHub sends the payload using Amazon SNS, and the payload finally ends up in the Amazon SQS. Jenkins just grabs the payload and triggers any jobs that have a matching github repository configuration.
Setup
The requirements are the following:
- Amazon Web Services subscription
- GitHub repository or repositories
- Jenkins
Amazon SQS configuration
As a first step, login to your AWS console, select SQS service and create a new queue.
Enter the queue name. Let’s call it
jenkins. Click onCreate Queue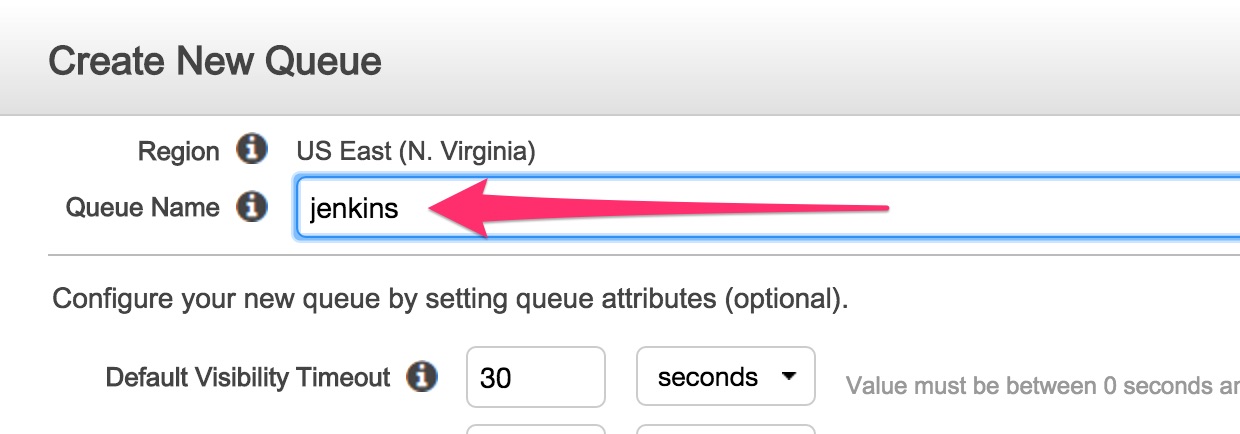
Select the newly created SQS queue and record the
ARN. You’ll need it later.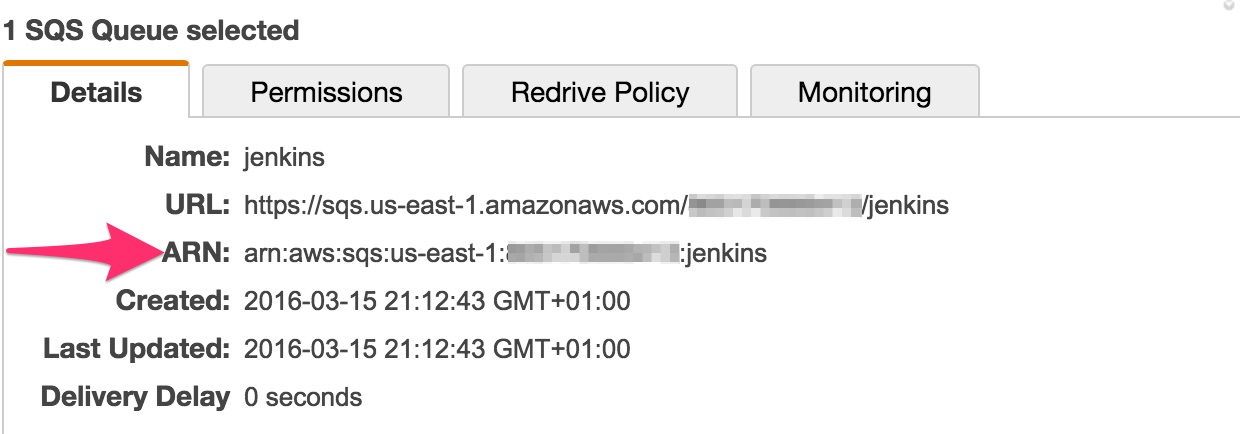
Amazon SNS configuration
Select SNS service in the AWS console and create a new topic.
Enter the topic name. Let’s call it
jenkins.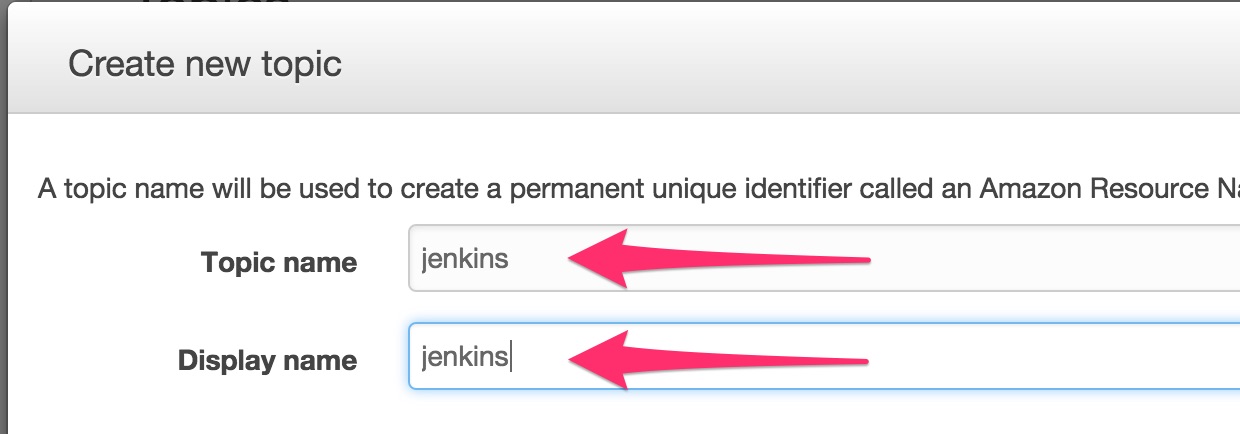
Select the newly created SNS topic and record the
ARN. You’ll need it later.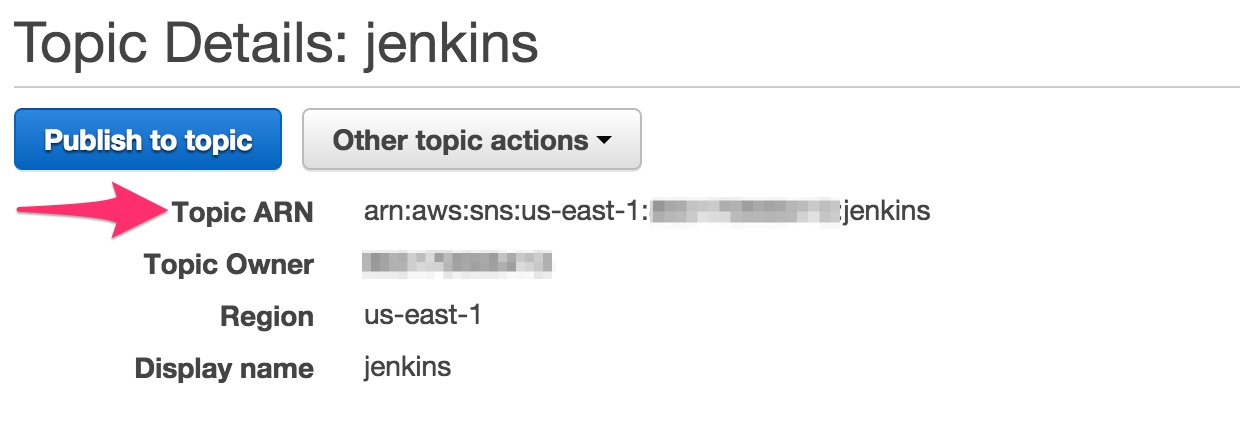
Amazon IAM configuration
It’s time to create an AWS Access Key ID and Secret Access Key for your jenkins and GitHub service. Select the IAM service and create a new user. By default generate an access key. Let’s call this user jenkins too. Record the credentials.
AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID=AKIA...
AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY=Aq9x...
Attach a right SQS/SNS managed IAM policy to this newly created user.
As a best practice, you should restrict the policy to have access only to the previously created SQS/SNS resources. You can read more about Amazon IAM policy
The Amazon Web Services configuration is now complete.
GitHub configuration
In case if your jenkins master has the rights to manage webhooks on GitHub, you can skip the next SQS configuration section. I usually don’t allow my jenkins to manage github hooks, because that requires administrative rights on a specific repo or even in the organisation.
GitHub webhook SQS configuration
Select your repository and select the
Settingstab.Select
Webhooks & services.Select
Add servicefrom the dropdown menu and selectAmazon SQS.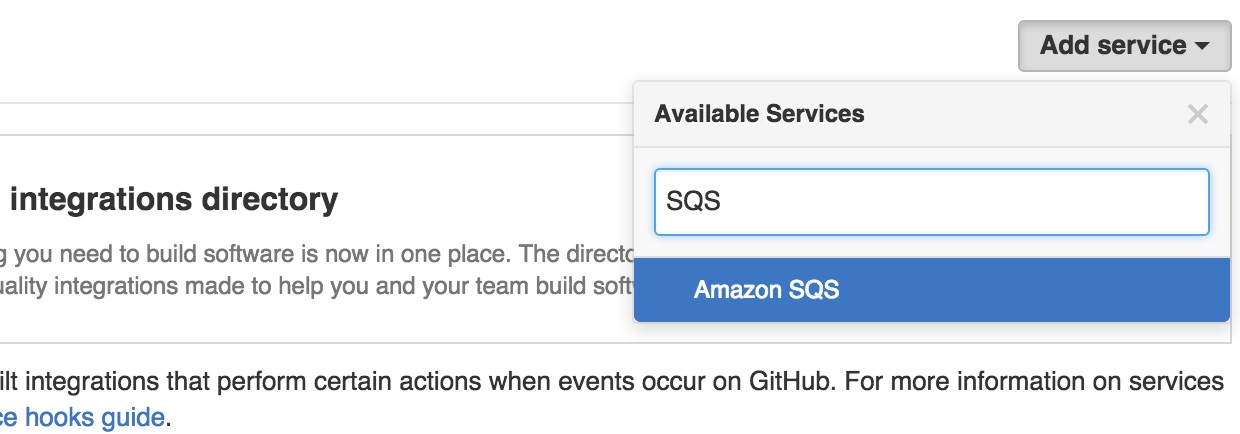
Enter the AWS credentials and the
ARNforSQSand save it.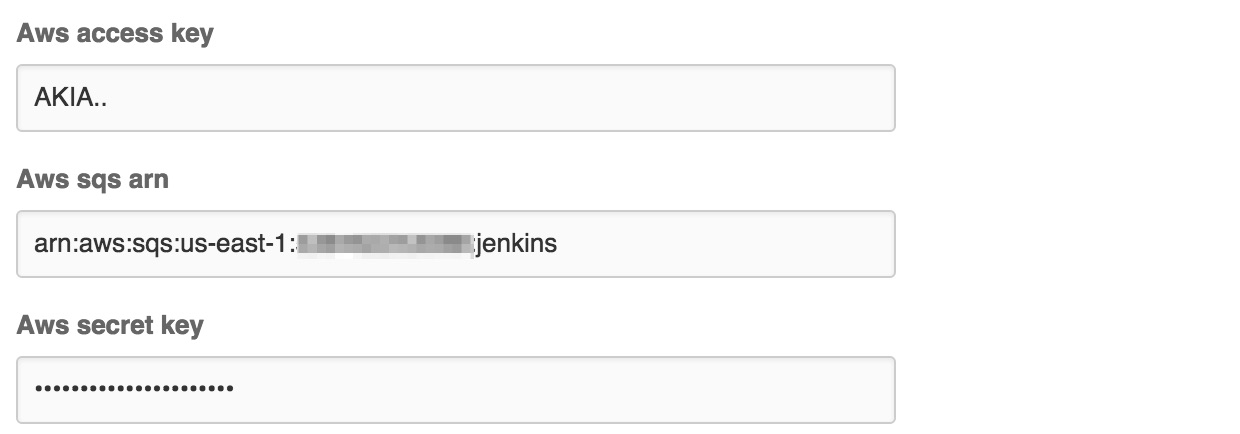
GitHub webhook SNS configuration
Select your repository and select the
Settingstab.Select
Webhooks & services.Select
Add servicefrom the dropdown menu and selectAmazon SNS.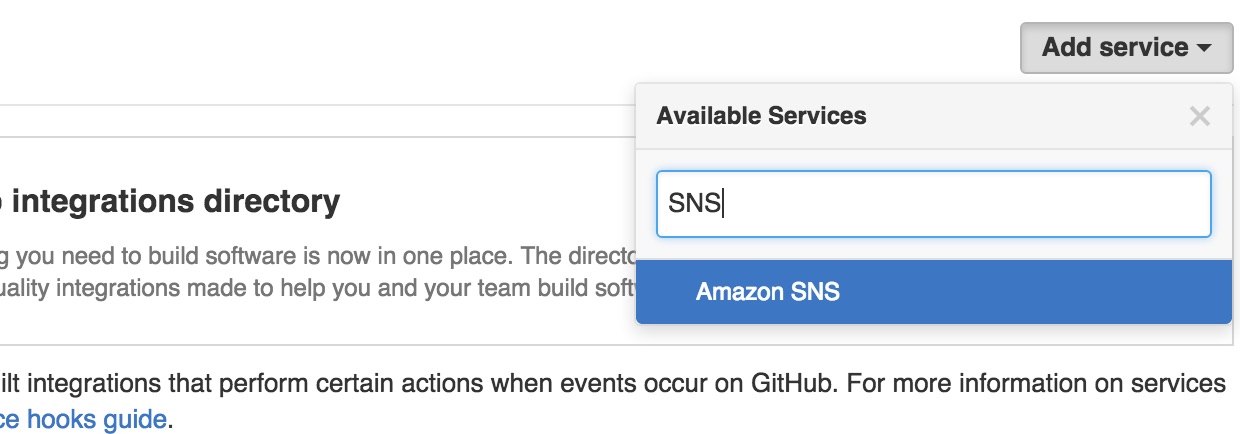
Enter the AWS credentials,
region, and theARNforSNSand save it.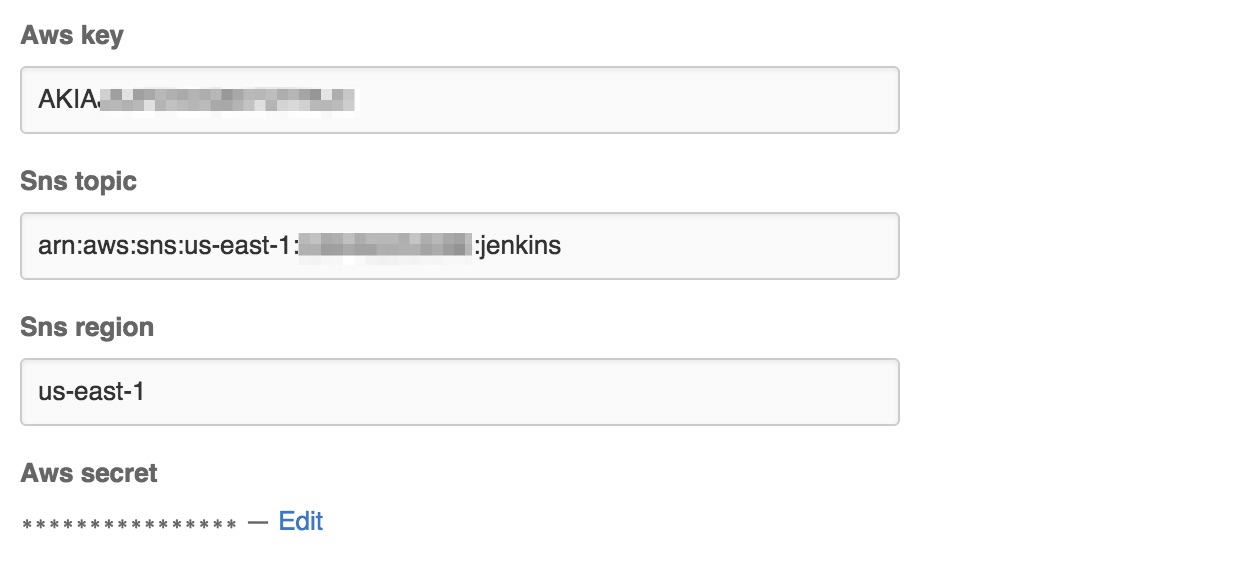
The GitHub configuration is now complete.
Jenkins general configuration
Install
GitHub SQS Pluginvia the plugin manager and restart your jenkins.Go to your jenkins’s configuration page
https://yourdomain/configureand locate theAmazon SQS Configurationsection.Enter the AWS credentials and the SQS queue name or URL. Hit
Test Accessto verify it’s working.Select
Manually manage GitHub SQS hookif your jenkins does not have access to manage webhooks on GitHub.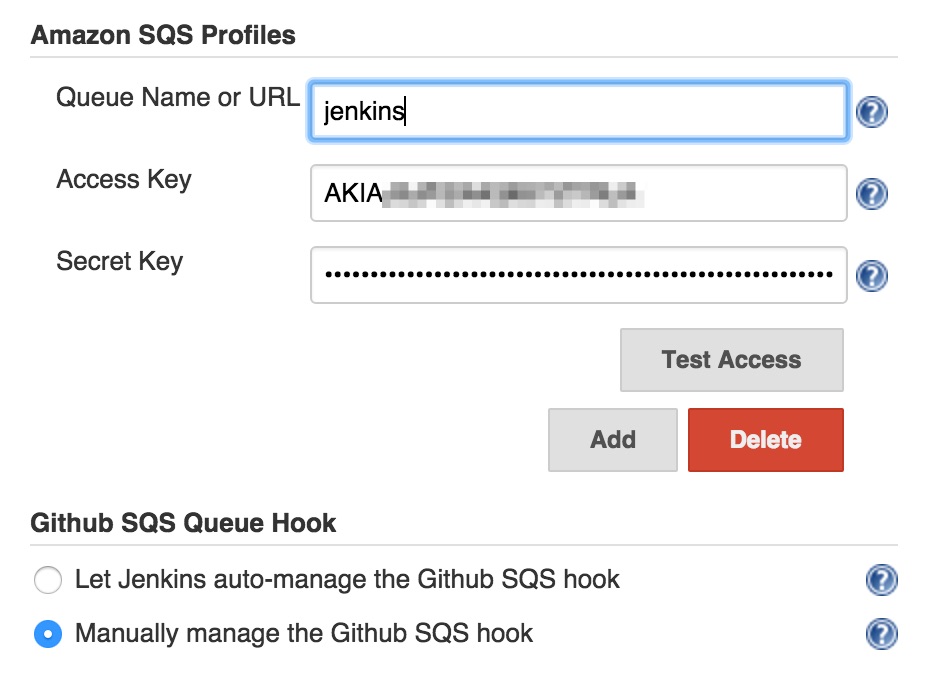
Jenkins job configuration
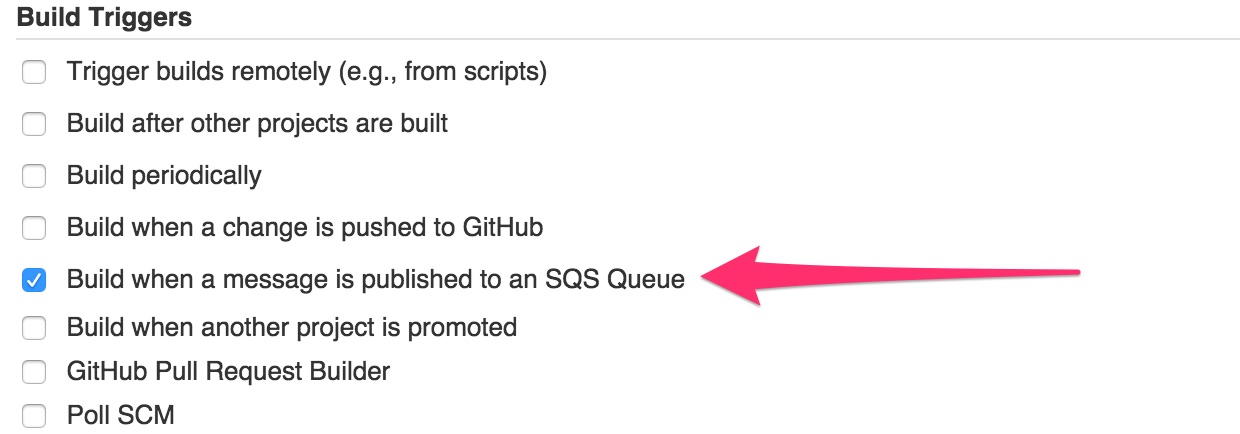
Go to your job’s configuration page and locate the Build Triggers section. Enable the Build when a message is published to an SQS Queue option and hit Save or Apply.
Profit
We’re all set. Your jenkins job is configured and will be triggered when somebody pushes a code to the repository. It clean and safe.